What is retinal vein occlusion?
Retina is a layer of tissue at the back of inner eye that converts light images to nerve signals and sends them to the brain. Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is a blockage of the small veins that carry impure or deoxygenated blood away from the retina. It is the second most common vascular disorder of the retina, next only to diabetic retinopathy.
What are the causes of retinal vein occlusion?
Retinal vein occlusion is most often caused by hardening of the arteries (atherosclerosis), which cross over veins in the Retina, and the formations of a blood clot. Hardened arteries press over veins and obstruct or occlude them.
Following are the risk factors:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Atherosclerosis
- Other eye conditions such as Glaucoma, vitreous hemorrhage
What are the signs and symptoms of retinal vein occlusion?
Due to blockage there is accumulation of the impure or deoxygenated blood, causing retinal haemorrhages and oedema which in turn leads to visual loss. Vision loss is usually sudden and may involve whole or partial loss of field of vision depending on the site of occlusion.
How is retinal vein occlusion diagnosed?
Detailed examination includes a dilated fundus examination, slit lamp biomicroscopy besides recording the visual acuity and intraocular pressure.
Following tests are commonly done as indicated:
- 3D OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography): It is a rapid non-invasive latest diagnostic tool used for the accurate diagnosis of retinal disorders that mainly involve the center of the retina called macula. The retina can be scanned at microscopic level and information can be obtained within minutes. Since the machine also has non mydriatic camera facility, it may be possible to even do the retina scans within minutes without even dilation of pupils in some patients.At NIO, we have one of the most advanced OCT systems (Topcon) which has ultra high resolution to detect any thickness change at the earliest.
- Flourescein Angiography:The ophthalmologist may decide to take this test if needed. It is a diagnostic test in which a dye is injected in the arm vein and retinal photographs are taken at regular intervals. This lets the doctor get an idea of the amount of leakage and the location of the abnormal retinal blood vessels. During the procedure, the patient may briefly feel some nausea. After the procedure, the patientís skin, eyes and urine may appear yellow for a few hours.
What treatment options are available for retinal vein occlusion?
While it is possible that the patient can regain vision even without treatment, their vision rarely returns to normal. There is no way to reverse or open the blockage.
You must consult an eye surgeon for treatment so as to prevent another blockage in the same or the other eye.
1. Intravitreal injections
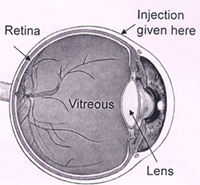
An intravitreal injection is given through the white part of your eye into the jelly (called vitreous) that fills the inside of your eye. Special drugs injected into the jelly spread to the retina (inner layer at the back of your eye) and other structures in your eye.
Your surgeon will assess and tell you if an intravitreal injection is suitable for you. However, it is your decision to go ahead with the procedure or not.
Types of intravitreal injections:
AVASTIN
AvastinTM was not initially developed to treat eye conditions. Based upon the results of clinical trials that demonstrated its safety and effectiveness, AvastinTM was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Once a device or medication is approved by the FDA, physicians may use it ìoff-labelî for other purposes if they are well-informed about the product, based on its use on firm scientific method and sound medical evidence, and maintain records of its use and effect. Ophthalmologists are using AvastinTM ìoff-labelî to treat AMD and other macular pathology.
OZURDEX is a disposable injection device containing a rod shaped implant. It contains dexamethasone. Its effect last for upto 180 days and it has been approved by the FDA.
LEUCENTIS is an Anti VEGF medication; it is a monoclonal antibody fragment and is approved by FDA.
TRIAMCINOLONE ACETONIDE is a Steroid. It is an off label drug. Its effect lasts up to 120 days.
To know more about intravitreal injections, click here
2. Laser Photocoagulation
This is an OPD procedure in which a laser beam (commonly 532 nm wavelength) is used to stop the growth of abnormal vessels and the leakage from the blood vessels. The aim of the treatment is to prevent further loss of vision and preserve the existing vision. The laser treatment is not aimed at improving the vision. The laser treatment is often completed in 3 to 5 sessions depending on the severity of the condition.
3. Vitrectomy/Retina surgery
If there is a vitreous or subhyaloid haemorrhage blocking the view or a tractional detachment exists, then a surgery in the form of vitrectomy is required.
The vitreous is a normally clear, gel-like substance that fills the center of the eye, giving it form and shape. Certain problems affecting the back of the eye may require a vitrectomy, or surgical removal of the vitreous. Vitrectomy is a very delicate surgery performed with an operating microscope and special needle-sized instruments where the vitreous gel, which is pulling on the retina, is removed from the eye and is usually replaced with silicone oil or gas bubble. Endo laser is carried out to seal the breaks causing the detachment. This procedure is done using the state-of-the-art Micro Incision Vitrectomy System (MIVS).
The benefits of MIVS surgery?
- Less pain as it is stitch-less surgery
- More comfort during the post operation recovery time.
- Quicker healing of the incision
- The wound is undetectable in 2 weeks time
- he procedure is quicker
To know more about MIVS click here
How can Retinal vein occlusion be prevented?
Retinal vein occlusion is a vascular disorder. The same measures used to prevent other blood vessel diseases, such as coronary artery disease, may decrease the risk of retinal vein occlusion.
Some of these measures include:
- Maintaining a low-fat diet and an ideal weight
- Not smoking
- Getting regular exercise
- Aspirin or other blood thinners may help prevent blockages in the other eye.
Controlling co-existing systemic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension is important in general, and can be helpful in preventing retinal vein occlusion.
NIO is one of the best eye care hospitals in Pune for treatment of retinal disorders. NIO offers quality health care services with the help of experienced doctors, and state-of-the-art facilities.
You can call our Healthcare team on 02025536369 / 41460100 if you have any queries regarding your childís eye.
Eye Care Learning




